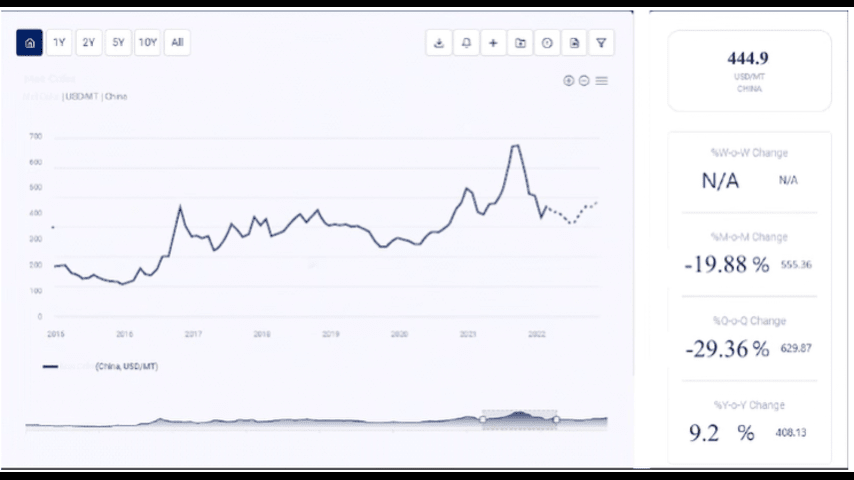
Coal remains a significant source of energy worldwide, used for electricity generation, steel production, and various industrial processes. Understanding the coal price chart is essential for energy companies, policymakers, investors, and other stakeholders to make informed decisions. This article explores the factors influencing coal prices and provides an overview of recent price trends.
1. Introduction to Coal
Coal is a fossil fuel extracted from the earth through mining and is categorized into different types based on carbon content and energy output, including anthracite, bituminous, sub-bituminous, and lignite. The price of coal is influenced by a variety of factors, including supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical events, production costs, environmental regulations, and technological advancements.
Enquire For Regular Prices: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/coal-price-trends/pricerequest
2. Factors Influencing Coal Prices
Several factors contribute to the fluctuations in coal prices. Understanding these factors is crucial for predicting price trends and making informed decisions.
- Supply and Demand: Global supply and demand dynamics significantly impact coal prices. Supply disruptions due to mining challenges, geopolitical conflicts, or natural disasters can lead to price spikes. Conversely, increased production and supply can drive prices down.
- Mining and Production Costs: The cost of mining and refining coal affects its market price. Factors such as ore grade, energy costs, labor expenses, and transportation costs influence production costs.
- Geopolitical Events: Political instability in key coal-producing countries, trade policies, and sanctions can affect the supply of coal, influencing its price.
- Environmental Regulations: Stricter environmental regulations and sustainability practices can impact coal production costs and availability, influencing prices. Regulations aimed at reducing carbon emissions and promoting cleaner energy sources affect the coal market.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in mining and refining technologies can impact the cost of coal production. Advances in cleaner coal technologies and carbon capture and storage also affect the market.
- Energy Transition: The global shift towards renewable energy sources and reduced reliance on fossil fuels can impact coal demand and prices.
- Currency Exchange Rates: Since coal is traded globally, currency exchange rates can affect prices. A stronger US dollar, for instance, can make coal more expensive for countries with weaker currencies.
- Market Speculation: Speculative trading and market sentiment can also cause short-term price fluctuations.
3. Recent Coal Price Trends
Recent coal price trends have been shaped by a combination of the factors mentioned above. Here, we examine the price trends over the past few years.
2019-2020:
- During this period, coal prices experienced moderate fluctuations. The primary drivers were changes in global supply and demand, as well as geopolitical events.
- In early 2019, prices were relatively stable, but began to decline towards the end of the year due to increased production and a shift towards cleaner energy sources.
- The COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 caused significant disruptions in supply chains and reduced industrial activity, leading to a further decline in coal demand and prices.
2021:
- As global economies began recovering from the pandemic, coal prices started to rise. The rebound in demand, particularly from the steel and electricity generation sectors, coupled with supply chain disruptions, pushed prices higher.
- The year saw increased coal prices due to a combination of strong demand, limited supply, and logistical challenges.
2022:
- Coal prices continued to trend upwards in early 2022, driven by ongoing supply chain challenges and robust demand from the industrial sector.
- The conflict between Russia and Ukraine exacerbated supply concerns, leading to further price increases, particularly in Europe.
- Throughout the year, prices remained volatile, influenced by geopolitical tensions, changes in energy policies, and fluctuations in production levels.
2023:
- The first half of 2023 saw some stabilization in coal prices as supply chains adapted and production levels normalized. However, prices remained elevated compared to pre-pandemic levels.
- Demand from the steel industry and developing economies continued to support higher prices.
- Geopolitical uncertainties, environmental regulations, and energy transition policies kept the market cautious, contributing to price volatility.
4. Regional Coal Price Trends
Coal price trends can vary significantly across different regions due to local supply and demand dynamics, mining costs, and government policies.
Asia:
- Asia, being a major consumer and producer of coal, experienced significant price variations. High demand from countries like China, India, and Japan influenced regional prices.
- China’s environmental regulations and mining policies played a crucial role in shaping the supply and price of coal.
Europe:
- Europe saw more pronounced price volatility due to its dependence on imported coal and the impact of environmental regulations. The transition towards renewable energy sources also affected coal demand and prices.
- The Russia-Ukraine conflict significantly impacted coal supply and prices in Europe, leading to higher costs and increased volatility.
North America:
- In North America, coal prices were influenced by domestic production levels, regulatory policies, and competition from natural gas and renewables.
- Government policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions and promoting cleaner energy sources influenced the coal market.
Australia:
- Australia, a major coal exporter, experienced price trends influenced by global demand, trade policies, and mining costs. Export demand from Asia played a significant role in shaping prices.
5. Future Outlook for Coal Prices
Predicting future coal prices involves considering various dynamic factors. Here are some key points to consider:
- Energy Transition: The global shift towards renewable energy sources and reduced reliance on fossil fuels is expected to impact coal demand and prices. However, coal is likely to remain an important energy source in developing economies for the foreseeable future.
- Technological Advancements: Continued advancements in cleaner coal technologies, carbon capture and storage, and mining efficiency could impact production costs and stabilize prices.
- Geopolitical Stability: Political stability in key producing regions and resolutions to ongoing conflicts could lead to more predictable supply and price trends.
- Environmental Regulations: Stricter environmental regulations and sustainability practices could impact coal production costs and availability, influencing prices.
- Supply Chain Adaptation: Efforts to diversify supply sources and improve mining efficiency could stabilize supply and reduce price volatility.
- Market Speculation: Speculative trading and investor sentiment will continue to influence short-term price fluctuations.
6. Conclusion
The price trend of coal is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including supply and demand dynamics, mining and production costs, geopolitical events, environmental regulations, technological advancements, energy transition, currency exchange rates, and market speculation. Recent trends have shown significant volatility due to the COVID-19 pandemic, geopolitical tensions, and supply chain disruptions.
Looking forward, the global energy transition, technological advancements, geopolitical stability, and environmental regulations will play crucial roles in shaping coal prices. Stakeholders must stay informed about these factors to navigate the market effectively and make informed decisions.
By understanding the various elements that drive coal prices, producers, consumers, and policymakers can better anticipate market changes and develop strategies to manage price risks and ensure a stable supply of this essential energy resource.